代码实现过程记录
具体代码见https://github.com/CanoeByGuitar/chenhui-lib
光线和各种物体求交

上面那个把法线从[-1,1]映射到[0,255,255]
带有Anti-aliasing的多物体求交


Lambertian Shading
// light
vec3 light_pos(0,4,-2);
float intensity = 1.f;
Light light(light_pos, intensity);
// World
Material *m = new Material(vec3(100, 100, 100));
SurfaceList world(nullptr);
world.add(std::make_shared<Circle>(Circle(m, vec3(0, 0, -1), 0.5)));
world.add(std::make_shared<Circle>(Circle(m, vec3(0, -100.5, -1), 100)));
vec3 ray_color(SurfaceList &world, Ray r, Light light){
Intersection inter1;
vec3 color(0, 0, 0);
if(world.getIntersect(r, 0.f, INF, inter1)){
auto p = inter1.point;
auto n = inter1.normal;
auto light_ray = Ray(p, light.pos - p);
auto l = light_ray.direction();
auto k_d = inter1.m->k_d;
Intersection inter2;
if(world.getIntersect(light_ray, 0.f, INF, inter2)){
// light cannot arrive at obj
}else{
auto I = light.intensity;
color += k_d * max(n * l, 0.f) * I;
}
}
return color;
}
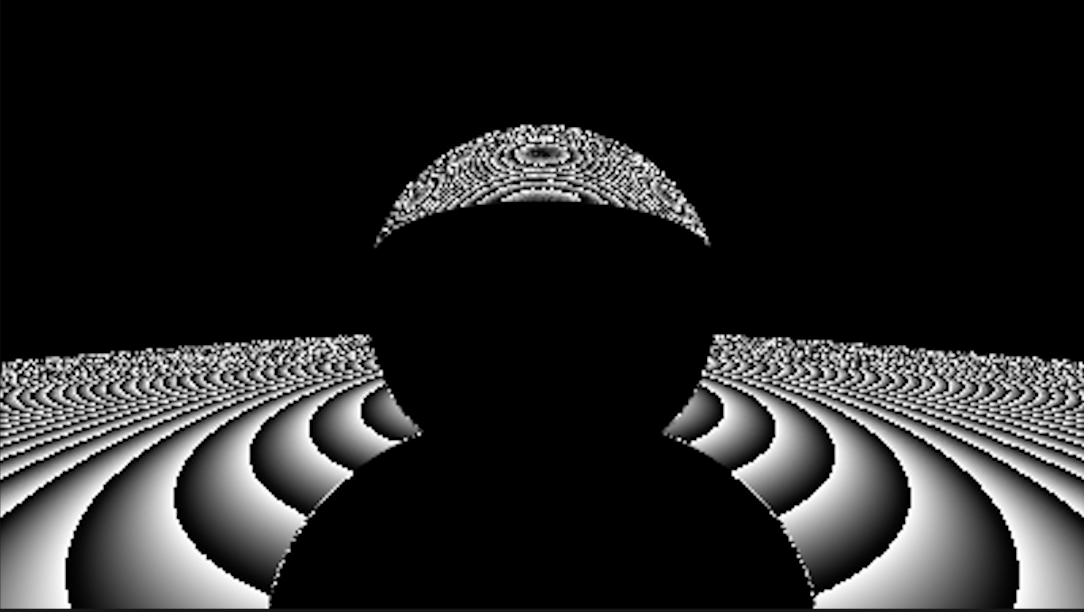

检查代码 材质里的k_d应该是[0,1]区间而不是[0,255]
Material *m = new Material(vec3(0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f));
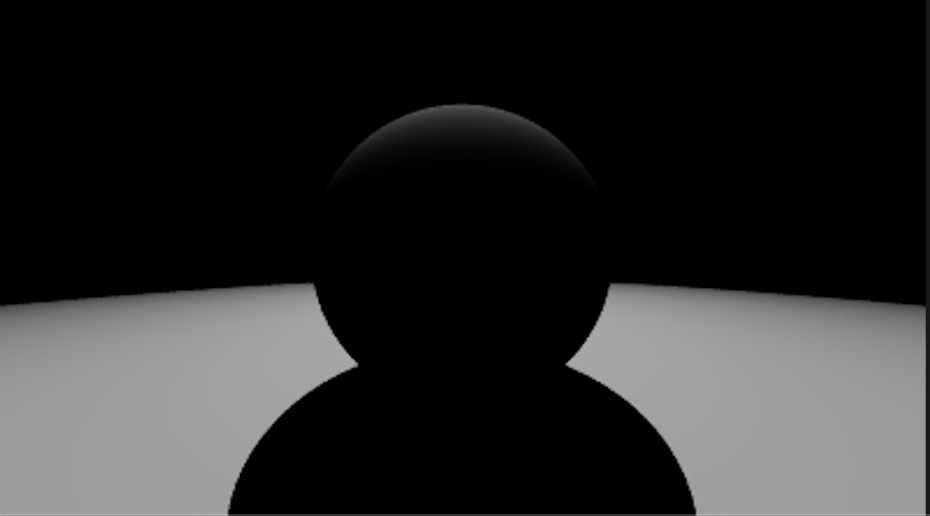

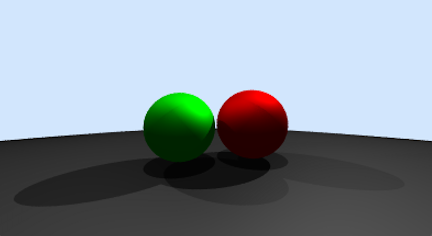
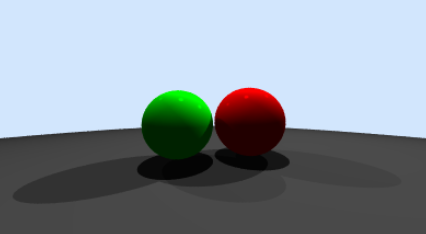
Blinn-Phong Shading
给输出color加了一个clamp,超过1的输出1,否则ppm会被大于255的数解析成黑的

下图的参数为:
// World
auto *m1 = new Material(vec3(1, 0, 0), vec3(1, 0, 0), vec3(1, 0, 0));
auto *m2 = new Material(vec3(0, 1, 0), vec3(0, 1, 0), vec3(0, 1, 0));
auto *m3 = new Material(vec3(0.25, 0.25, 0.25), vec3(0.25, 0.25, 0.25), vec3(0.25, 0.25, 0.25));
SurfaceList world(nullptr);
world.add(std::make_shared<Circle>(Circle(m1, vec3(0.42, -0.08, -1.5), 0.4)));
world.add(std::make_shared<Circle>(Circle(m2, vec3(-0.35, -0.1, -1.3), 0.35)));
world.add(std::make_shared<Circle>(Circle(m3, vec3(0, -100.5, -1), 100)));
// light
std::vector<Light> light_list;
light_list.emplace_back(vec3(-4, 4, -3), 0.2f);
light_list.emplace_back(vec3(4, 4, -3), 0.5f);
light_list.emplace_back(vec3(0, 6, 0), 0.3f);
vec3 ray_color(SurfaceList &world, Ray r, const std::vector<Light> &light_list) {
Intersection inter1;
vec3 color(0, 0, 0);
if (world.getIntersect(r, 0.f, INF, inter1)) {
auto p = inter1.point;
auto n = inter1.normal;
auto v = -r.direction();
auto k_d = inter1.m->k_d;
auto k_s = inter1.m->k_s;
auto k_a = inter1.m->k_a;
// ambient shading
float I_a = 0.2;
color += k_a * I_a;
for (auto light: light_list) {
auto light_ray = Ray(p, light.pos - p);
auto l = light_ray.direction();
auto h = unit_vec((v + l));
Intersection inter2;
if (world.getIntersect(light_ray, 0.f, INF, inter2)) {
// light cannot arrive at obj
} else {
auto I = light.intensity;
color += k_d * max(n * l, 0.f) * I + k_s * I * pow(max(0.f, n * h), 10);
}
}
}else{
// background color
return vec3(0.847, 0.914, 0.996);
}
return clamp(color, 0, 1);
}
调整下面的p得到不同的材质
L = k_d* I * max(0,n.dot(l))+ k_s* I * max(0,n.dot(h))^p // p是为了加速从高光到消失的变化效果的
Math
点到直线距离
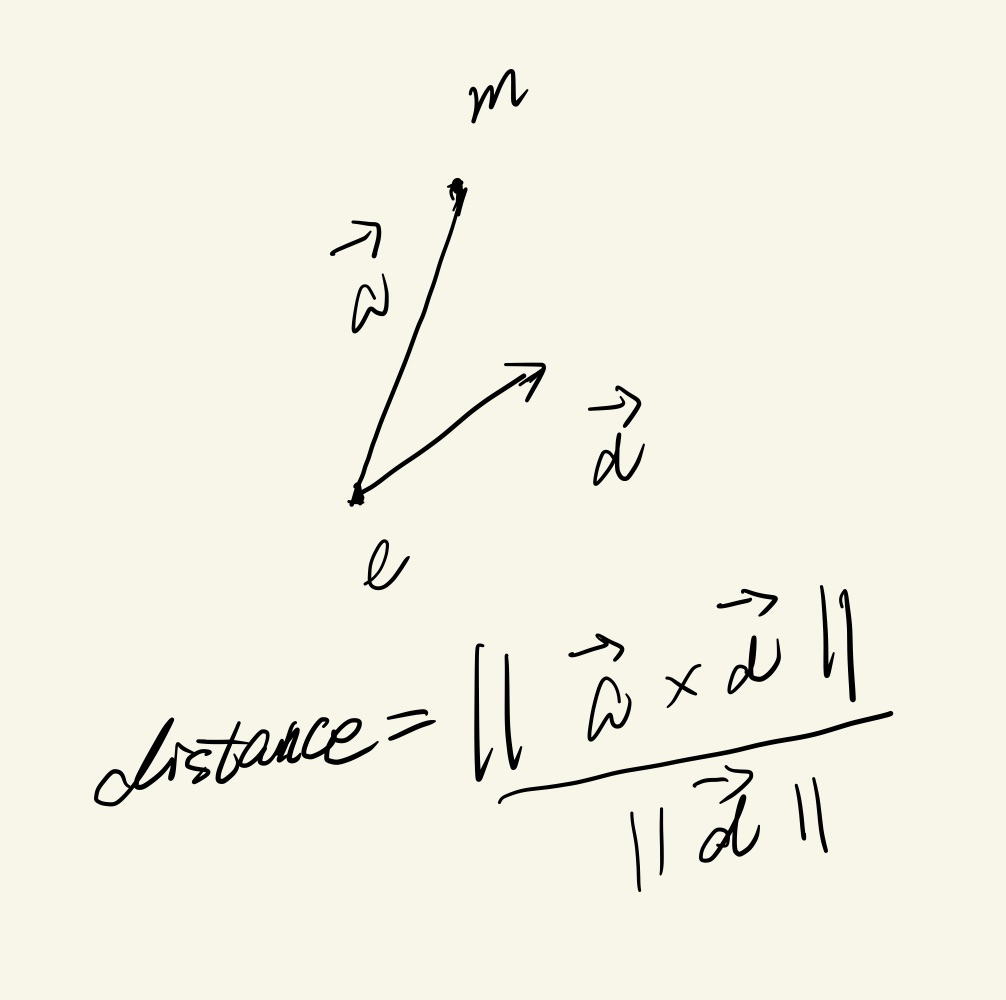
计算行列式
LU分解 L下三角 U上三角
变换矩阵
首先注意,正交矩阵包括旋转和镜面反射两种情况
det(A) == 1 ==> rotation
det(A) == -1 ==> reflection
任意一个对成矩阵A,都表示沿着某一个方向(x'oy')进行放缩,x'oy'由特征向量组成
==symmetric matrices can be decomposed via eigenvalue diagonalization into a rotation times a scale times the inverse-rotation==
相似对角化$ A = R S R^{T} $
旋转 ==> 放缩 ==> 转回来
3D 旋转矩阵
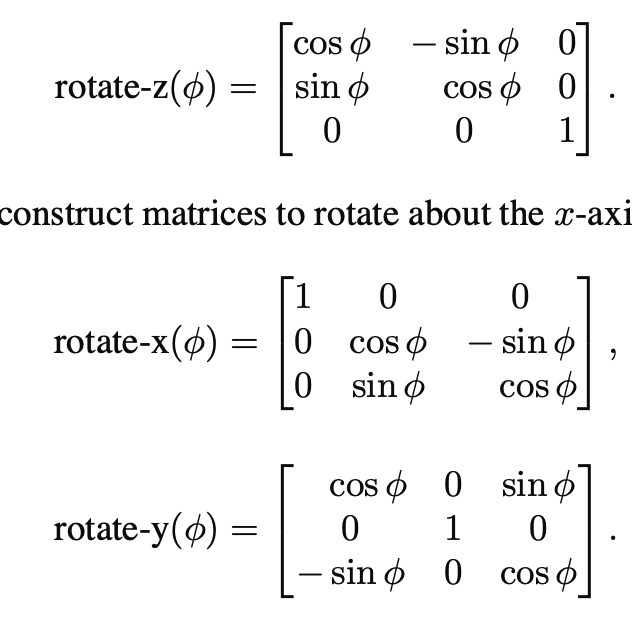
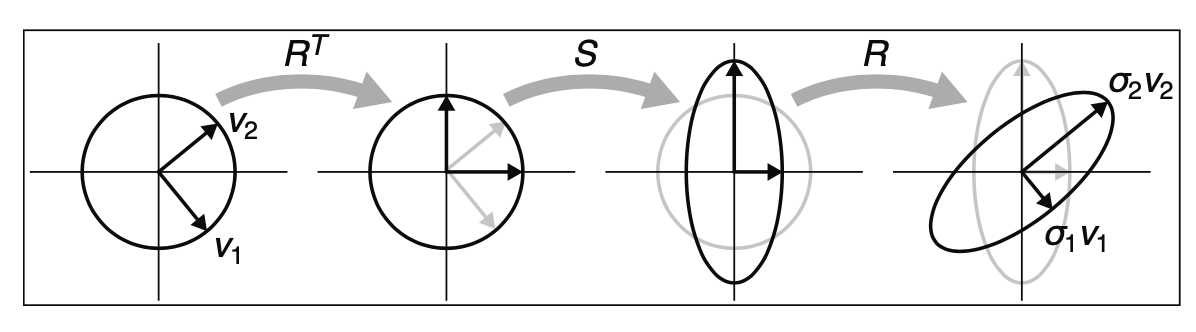
SVD
singular value decomposition
==every matrix can be decomposed via SVD into a rotation times a scale times another rotation==
如何解决正交矩阵不一定是旋转矩阵的问题?(Dynamic Deformables P181)
手算SVD分解:
对称矩阵正交相似化,求特征值、特征向量, 特征值开根就是B,原则上统一取B为正的。
极分解:
任意一个矩阵A可以分解为
其中R是 正交矩阵, S是对称半正定矩阵
分解过程借助于SVD
令,
因为U V为正交矩阵,所以也是正交矩阵(乘自己转置为E)
B是对角阵,且正定,所以S对称正定。
实现(JacobiSVD)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/459369233
Matrix Computation(2013) p447
- 先算极分解, ,得到对称矩阵S
- 对S进行Jacobi(Givens)旋转对角化,去掉非主对角的非零元素
齐次坐标(homogeneous coordinates)
点 ==> (x, y, 1)
方向 ==> (x, y, 0)
Ray tracing
for each pixel do
compute view ray
find first hit object and its norml n
set pixel color from hit point, light, normal n
Gen rays
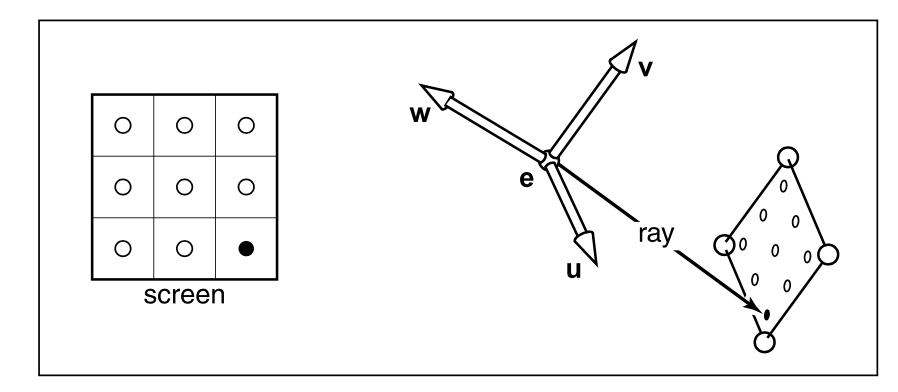
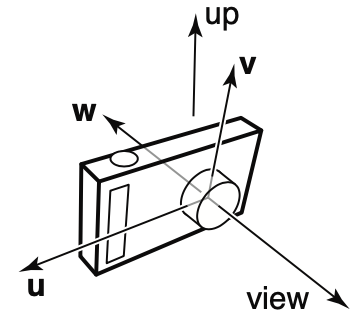
相机的view port是w的反方向(Opengl里也是如此)。
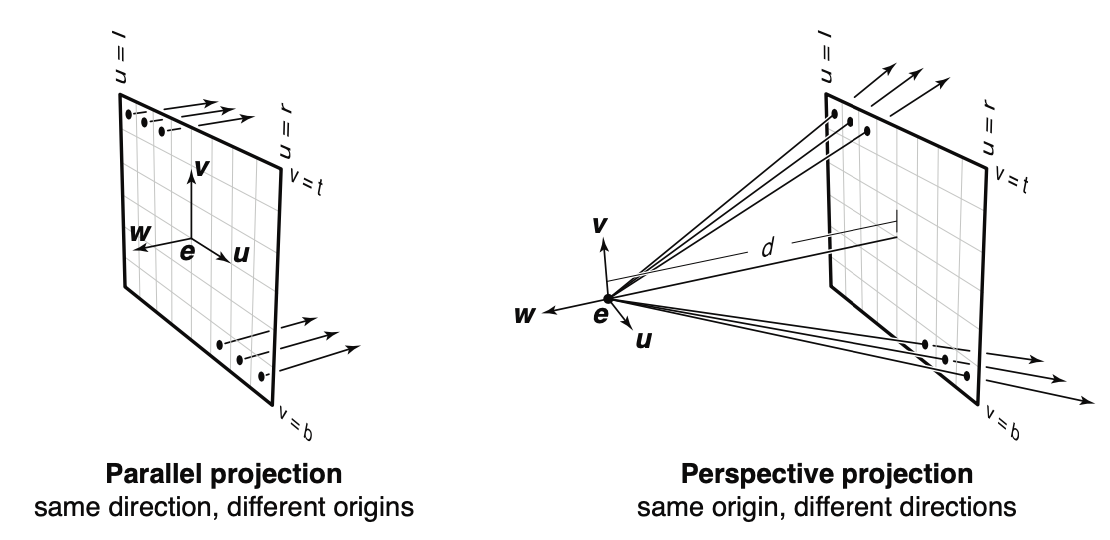
Orthographic view
// input [l,r,b,t, nx, ny, u, v, w]
// pixel (i,j) ==> position coordinates
px = l + (r - l) / nx * (i + 0.5)
py = b + (t - b) / ny * (j + 0.5)
ray.direction = -w
ray.origin = e + px * u + py * v
Perspective Views
px = l + (r - l) / nx * (i + 0.5)
py = b + (t - b) / ny * (j + 0.5)
ray.direction = -d * w + px * u + py * v;
ray.origin = e;
Ray-Object intersection
Ray-Sphere
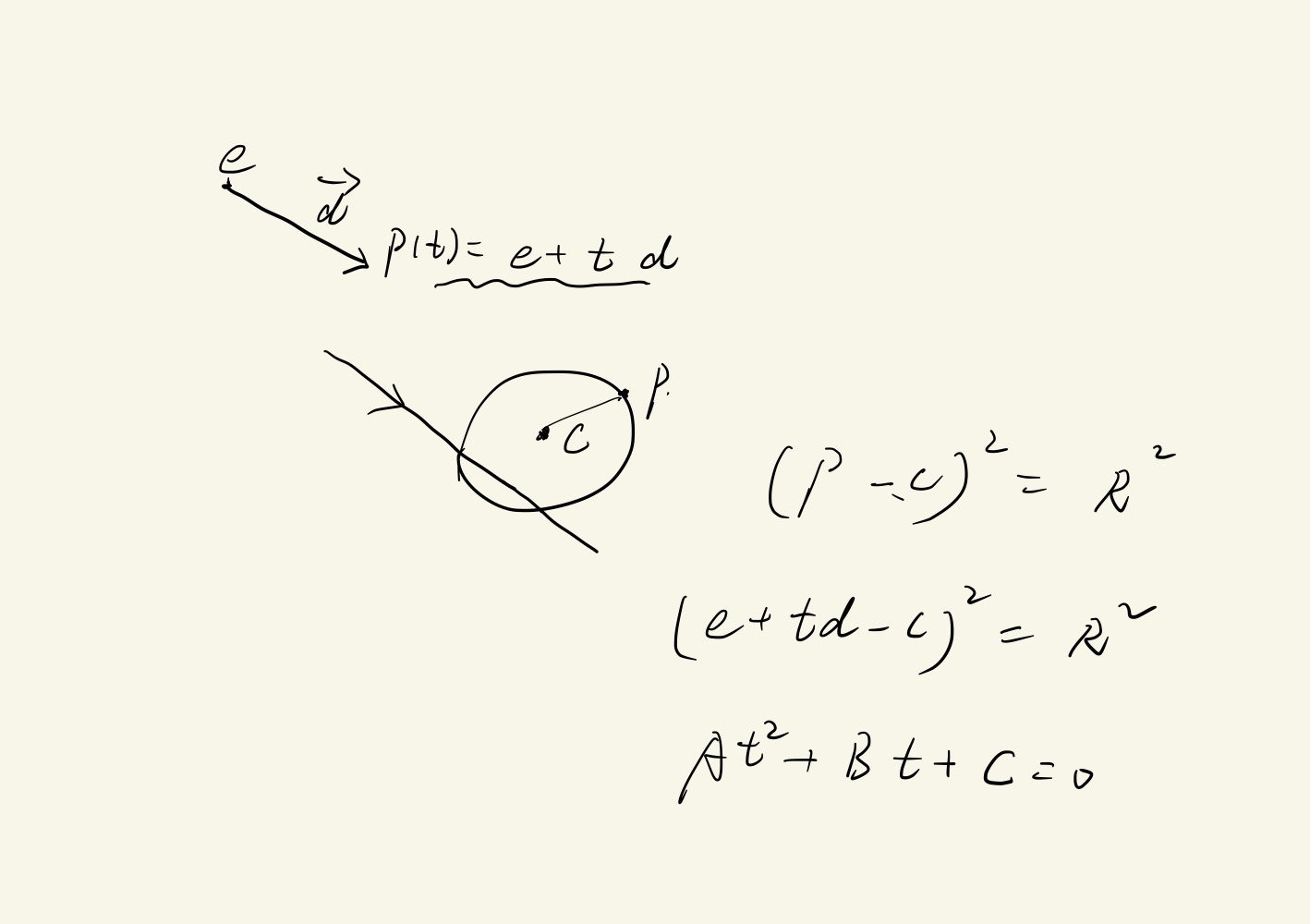
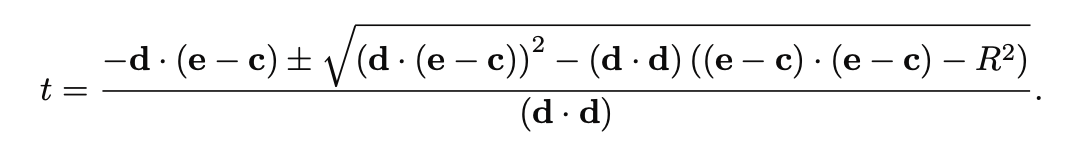
Ray-Triangle
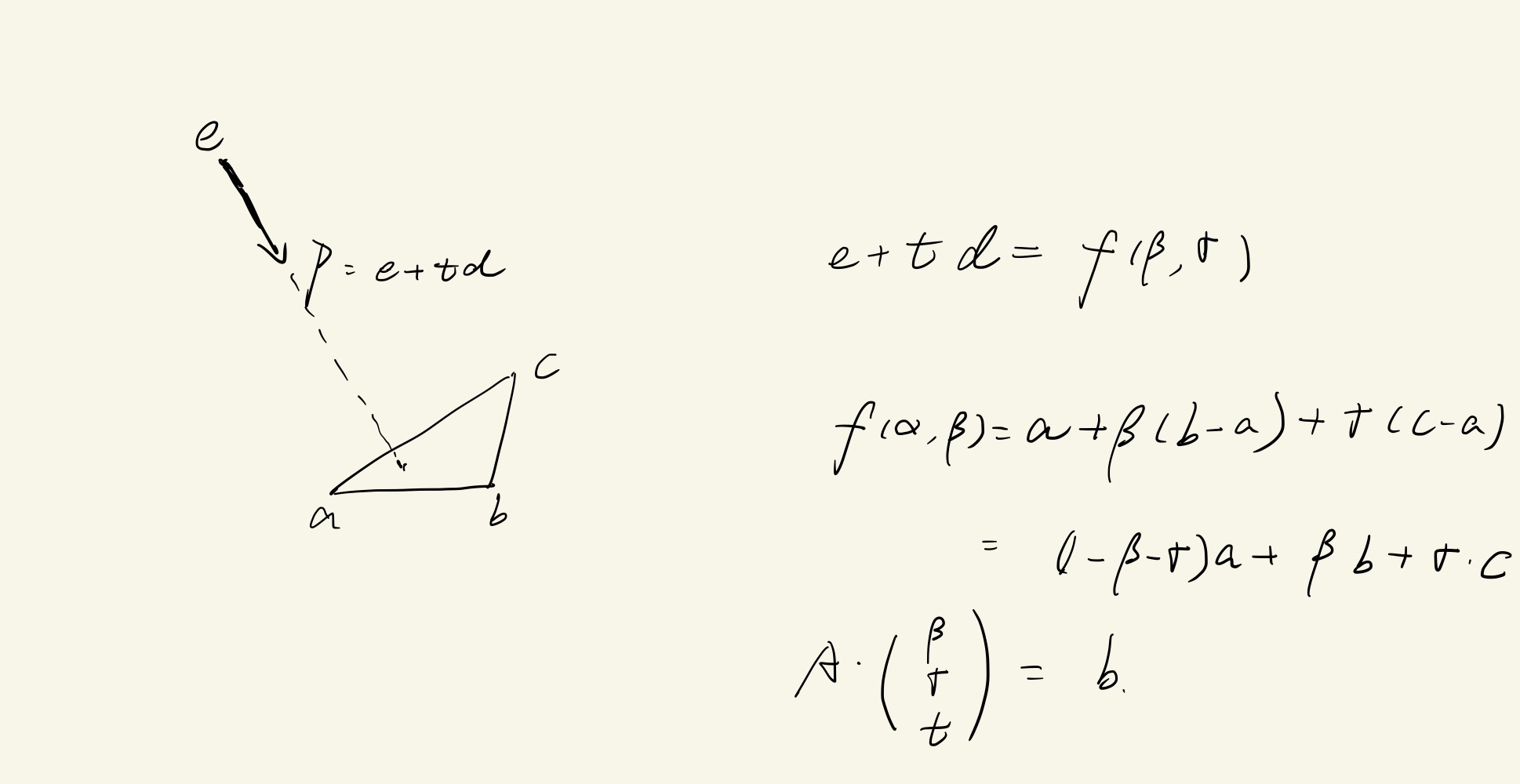
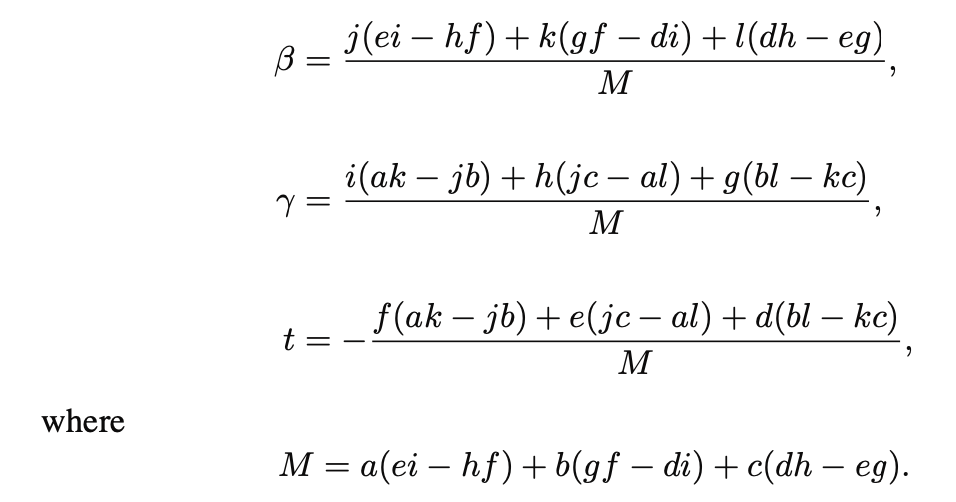
// ray-triangle intersection
compute t
if(t < t0 || t > t1) return false;
compute gamma;
if(gamma < 0 || gamma > 1) return false;
compute beta;
if(beta < 0 || beta > 1 - gamma) return false;
return true;
Ray-Polygon
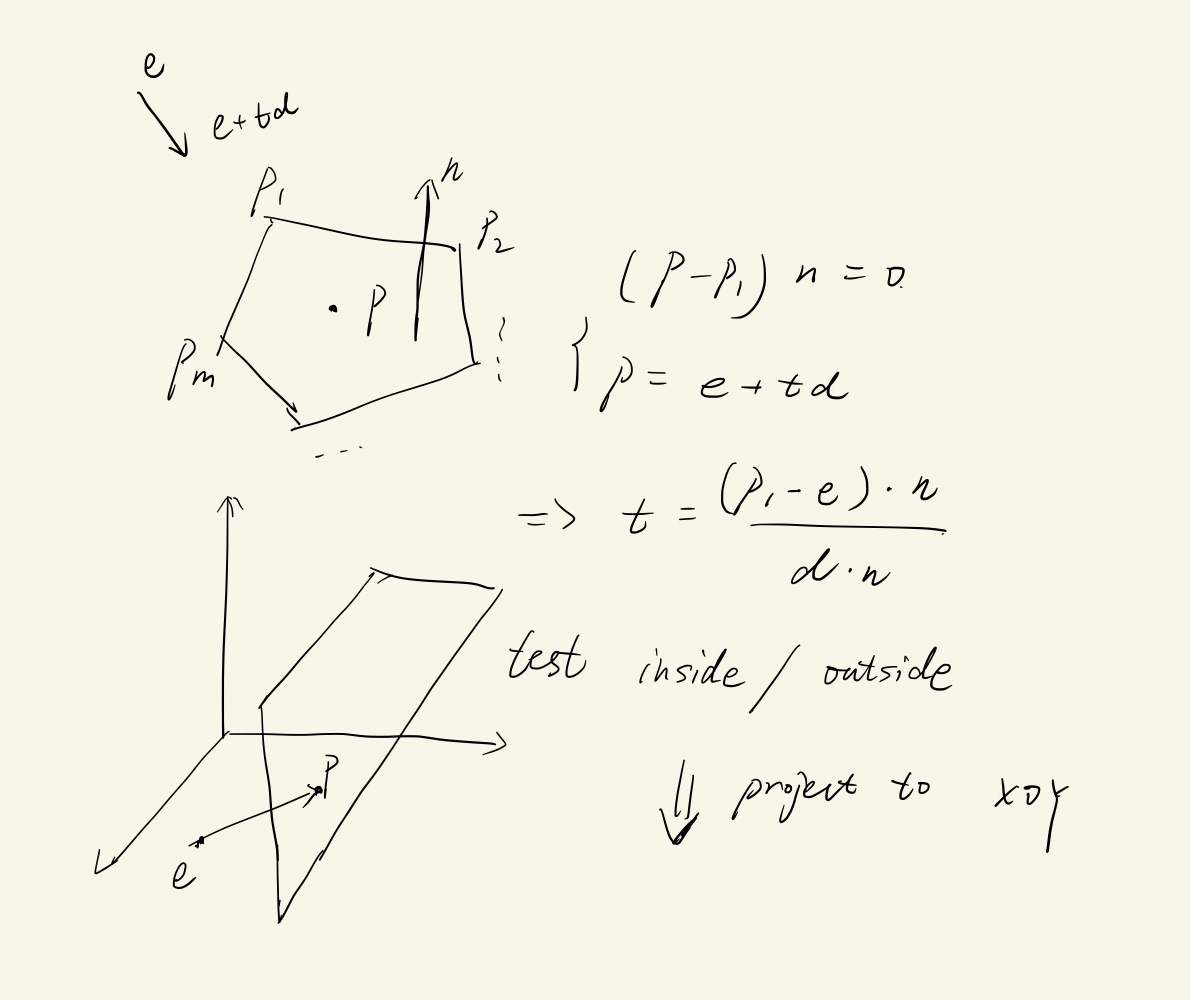
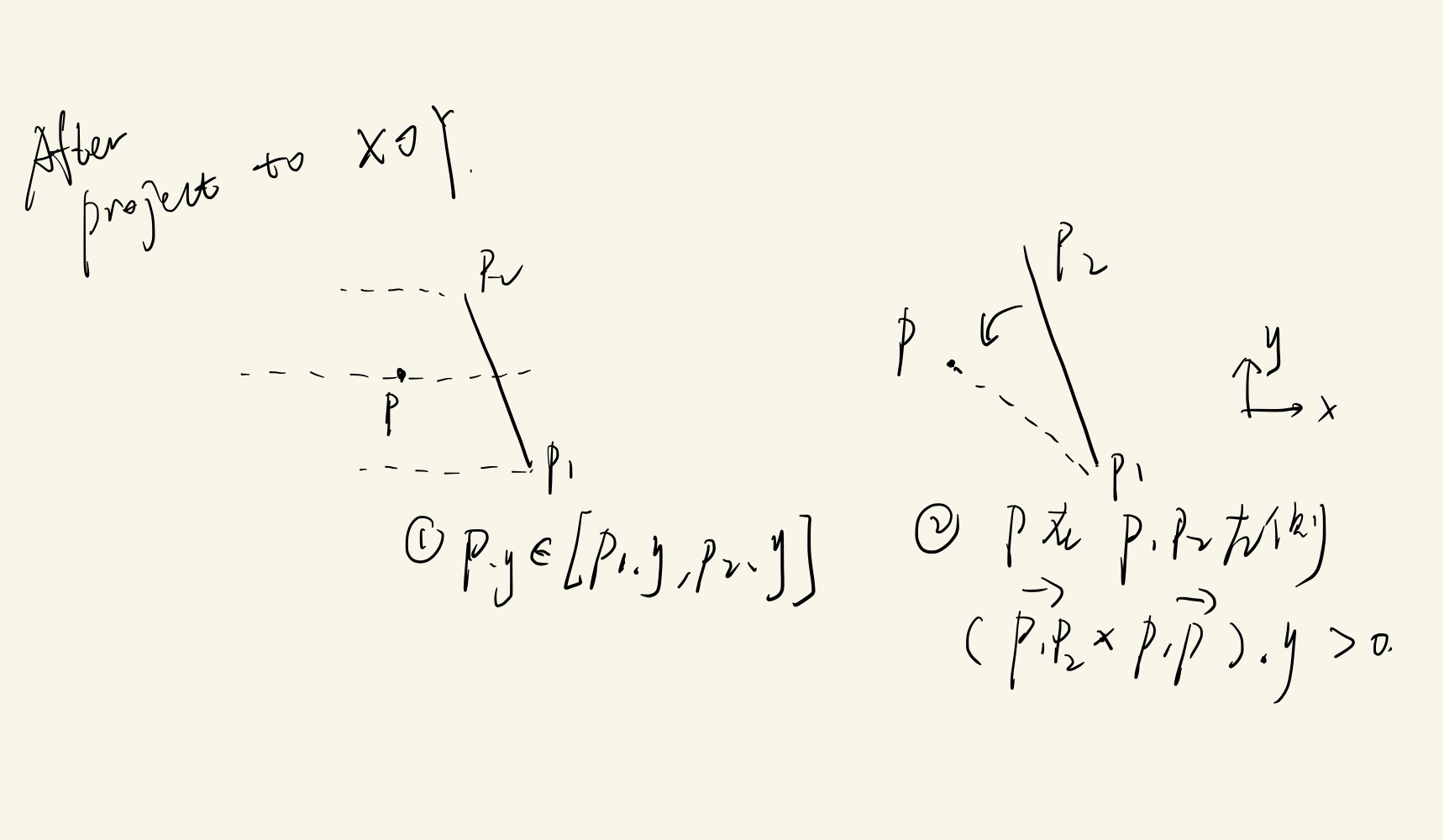
2D判断p在多边形内/外
ray from p intersects with polygon boundary
count the hit number h
if(h is odd) return inside
else return outside
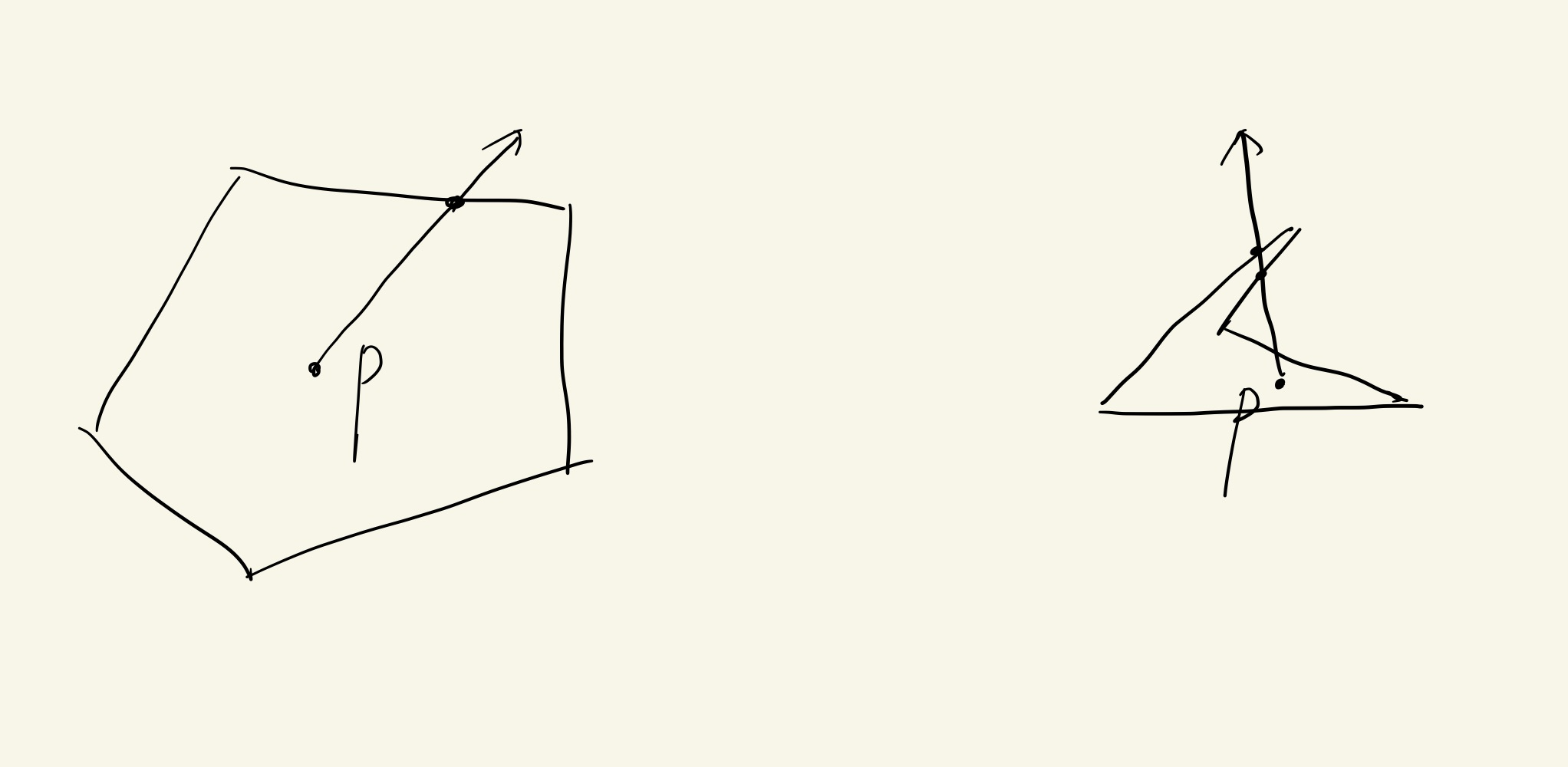
A group of Objects
// input [t0, t1] ray
intersection{
bool hit = false
for(each object o: group){
if(o intersets ray in t && t >= t0 && t < t1){
hit = true;
hit_obj = o;
t1 = t;
}
}
return hit
}
Shading
important variables:
light direction l
view dirction v
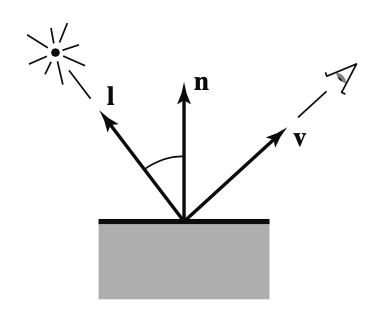
Lambertian Shading
落在surface上的光的量只和入射角度相关(view independent 不考虑人眼位置看到的光的不同)
垂直的时候 光最多
相切的时候 光为0
两者之间时,和入射光与face normal的夹角theta成正比。
L = k_d * I * max(0, n.dot(l));
// k_d: diffuse coef / surface color 3 channels
// I: light intensity 3 channels
// n: unit face normal
// l: unit light dir
Blinn-Phong Shading
在Lambertian的基础上额外考虑高光(Phong和Blinn两个人分别完成和改进)
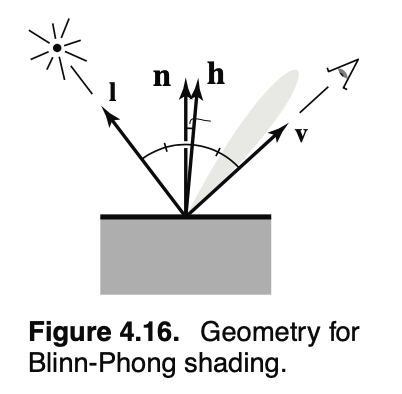
h = (v + l).norm()
// Labert diffusion + specular
L = k_d* I * max(0,n.dot(l))+ k_s* I * max(0,n.dot(h))^p // p是为了加速从高光到消失的变化效果的
Ambient Shading
然而在早期的blinn-phong模型下,没有被光源直接照射的地方就是纯黑的,因为blinn-phong不考虑间接光,所以一个讨巧的方法是,
给surface表面默认附上一个颜色,叫ambient shading
以上三块整体构成blinn-phong模型
L = diffusion + specular + ambient(环境光)
L = k_d* I * max(0,n.dot(l))+ k_s* I * max(0,n.dot(h))^p + k_a * I_a // 可以所有的surface k_a都相同,也可以不一样
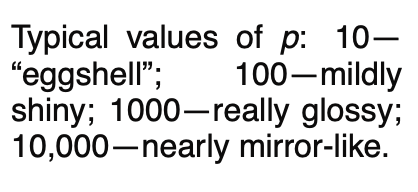
Multiple Point Lights
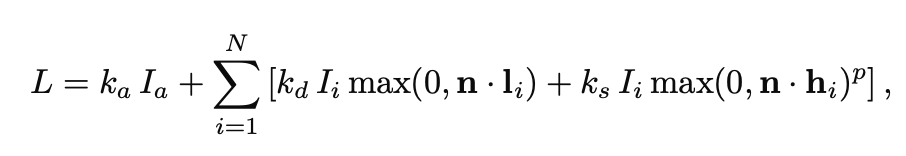
疑问:怎么设定, 不会产生过爆吗?
A ray tracing program
for each pixel{
compute viewing ray r
if(r hits a object with t in [0, +inf]){
compute normal n;
evaluating shading and set color to the pixel
}else{
set pixel to background color
}
}
OOP类设计
class surface: geometry{
virtual bool hit(ray r+td, real t0, real t1, hit_record rec);
virtual box bounding_box()
private material *mtl;
}
class sphere:surface{
box bounding_box(){
vec3 min = center - vec3(radius, radius, radius);
vec3 max = center + vec3(radius, radius, radius);
return box(min, max);
}
}
Shadows
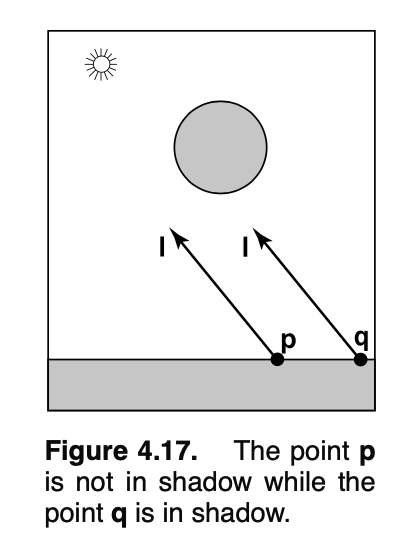
shadow ray(区分与view ray) 用来判断是否在阴影中(如果hit了object,则在阴影中)
p+t*l, t in [0,+inf)
// 实践中通常为
t in [kesi, +inf] // 防止数值误差导致intersect with p本身在的平面。
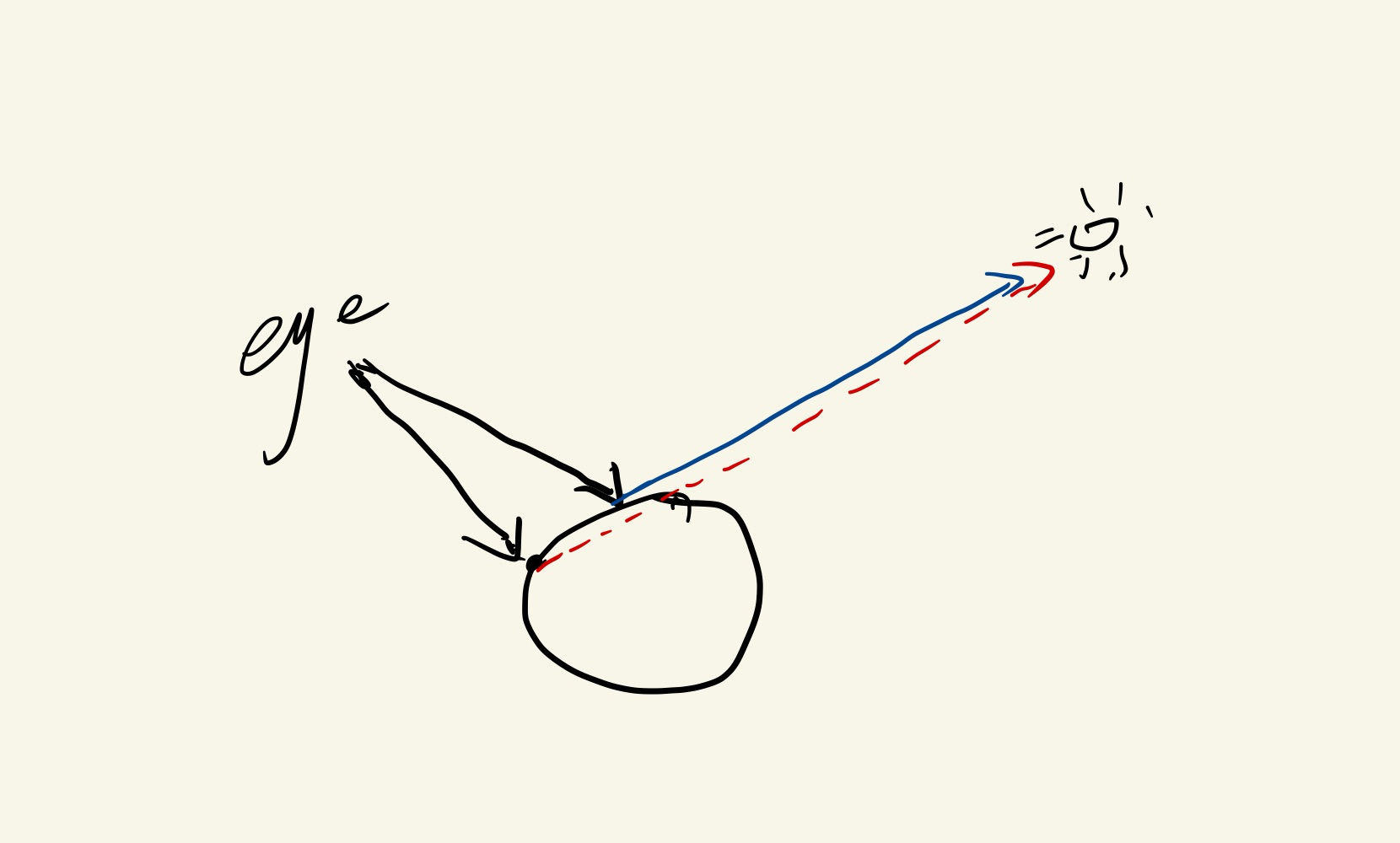
至此,更新ray tracing中计算某个像素颜色的算法
raycolor(e+t*d, t0, t1){
if(hit(e + t*d, t0, t1, &rec)){
p = e + (hit_record).t * d;
color c = rec.k_a * I_a; // ambient light
// 判断能否被光源照到
if(not hit(p + s*l, kesi,inf, &second_record)){
// 没有阴影
vec3 h = (l.norm() + (-d).norm()).norm();
c = c + rec.k_d*I*max(0, n*l) + rec.k_s * I * (n * h)^(rec.p);
}else{
// 有阴影不做其他处理
}
}else{
// 没有看到物体
return background;
}
}
Viewing
Object Space ==> World Space ==> Camera Space ==> Canonical View Volume ==> Screen Space
M V P viewport transformation
一些别称:
Canonical View Volume: Clip Space, Normalized device coordinates(NDC)
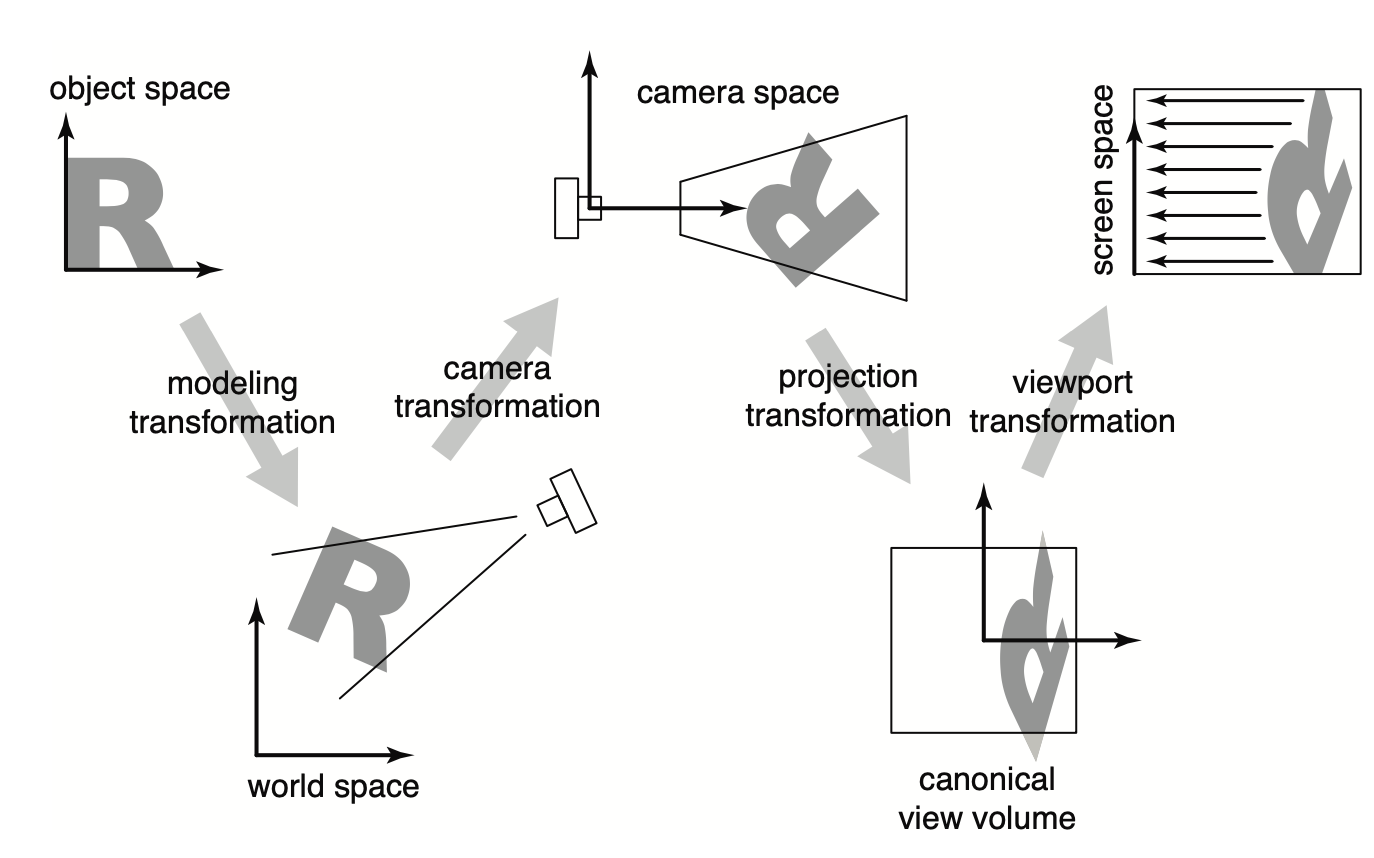
Viewport Transformation
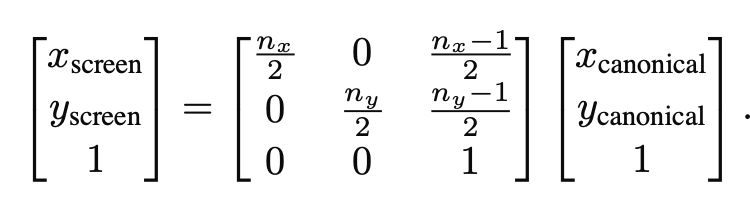
加上z轴,让z保持不变
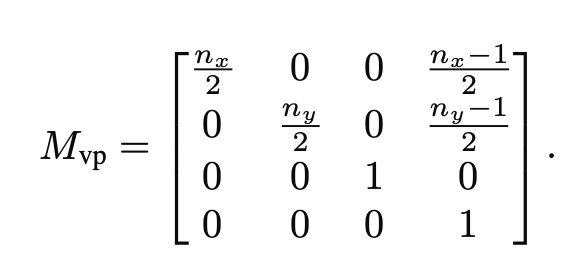
Projection transformation
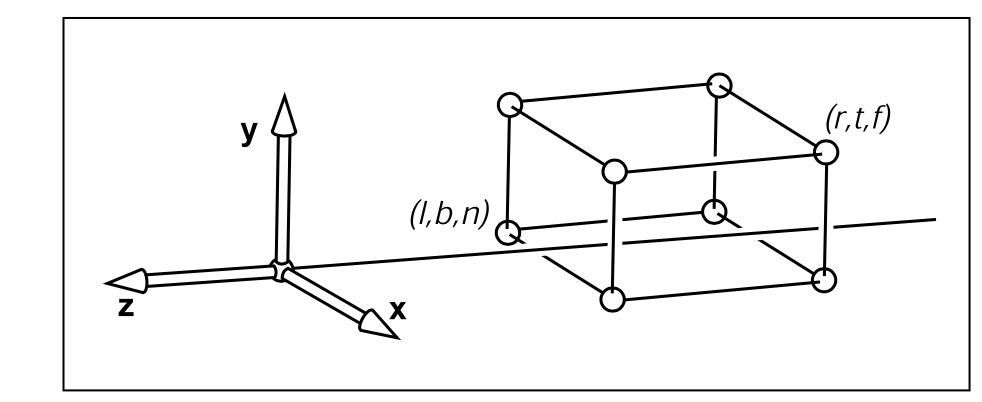
Orthographic
前者取决于用户设定
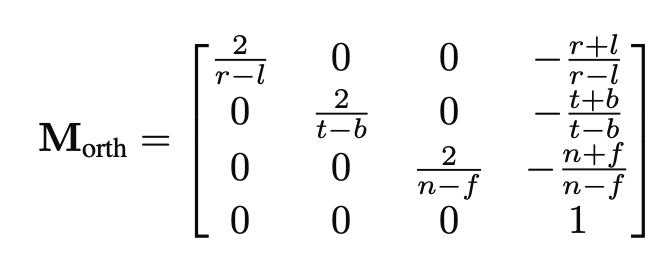
e.g:
n = -0.01
f = -150
Projective
View(Camera) transformation
world space[x,y,z] ===> camera space[u, v, w]
[u, v, w] can be generated from camera info:
- eye position: e
- gaze direction: g
- view-up vector: t 只是把观察者的头部分成左右两个部分
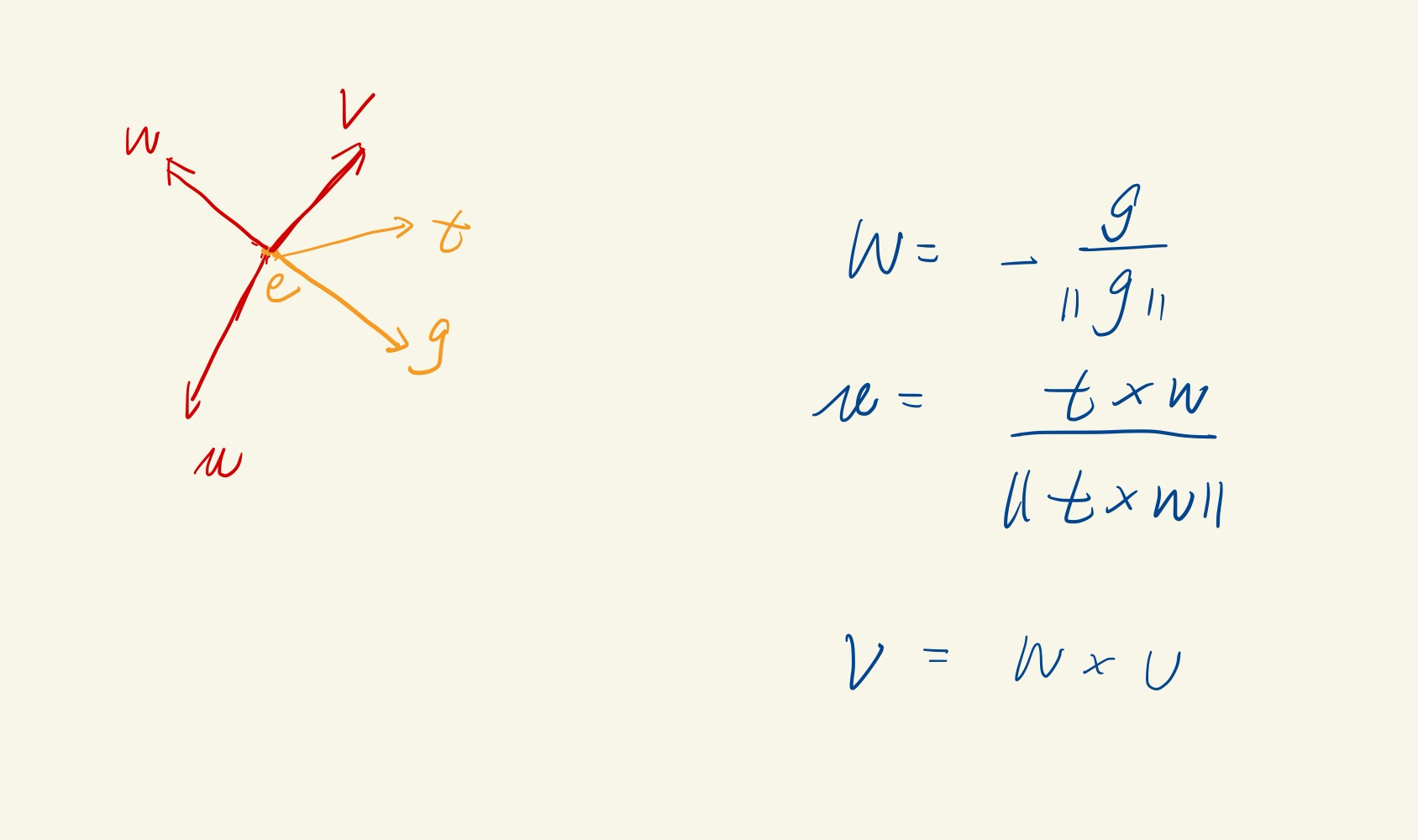
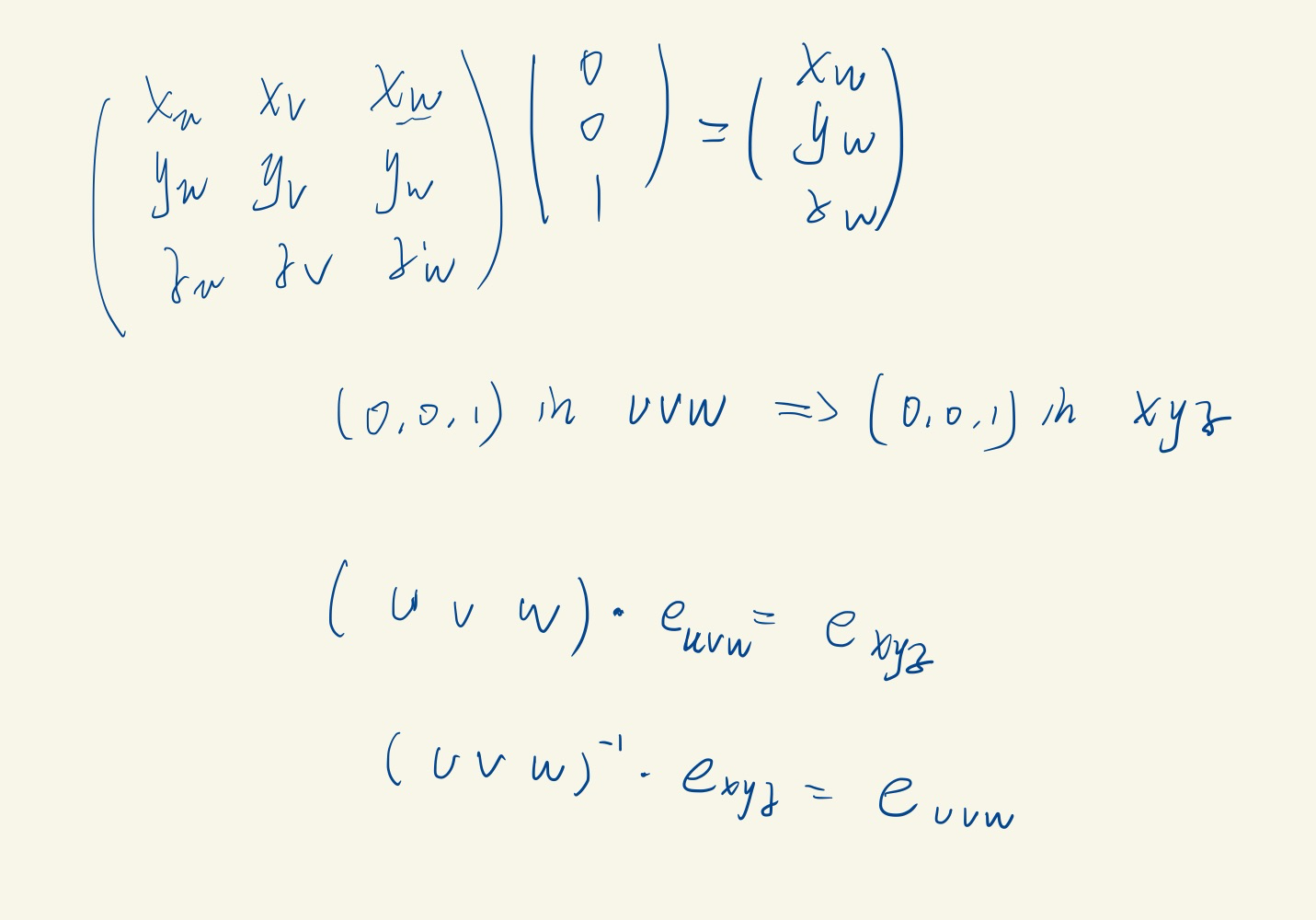
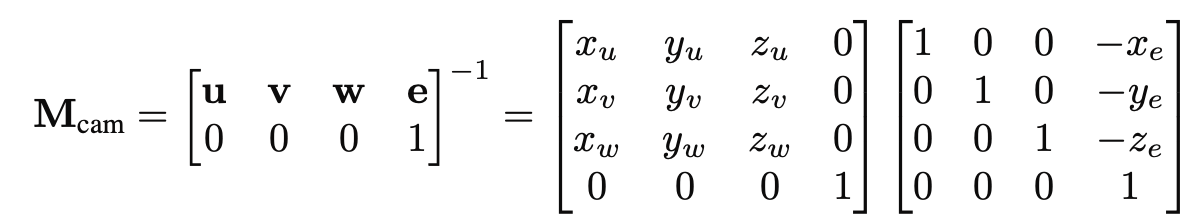
可以理解成先移动-e到原点再旋转