Before Reading
本项目只作为课程作业。项目地址
总体模块
几何模块为公共的几何体,如line、circle、AABB、triangle、mesh等,并有相应的几何变换和空间加速方法。
物理和渲染模块都继承几何模块的类,物理模块可能有额外的质量、速度、形变梯度等数据,渲染模块有额外的三角形剖分、shader、VAO等数据
使用观察者模式和std::function实现,物理模块对Geometry产生更新时通知渲染模块进行动态渲染。
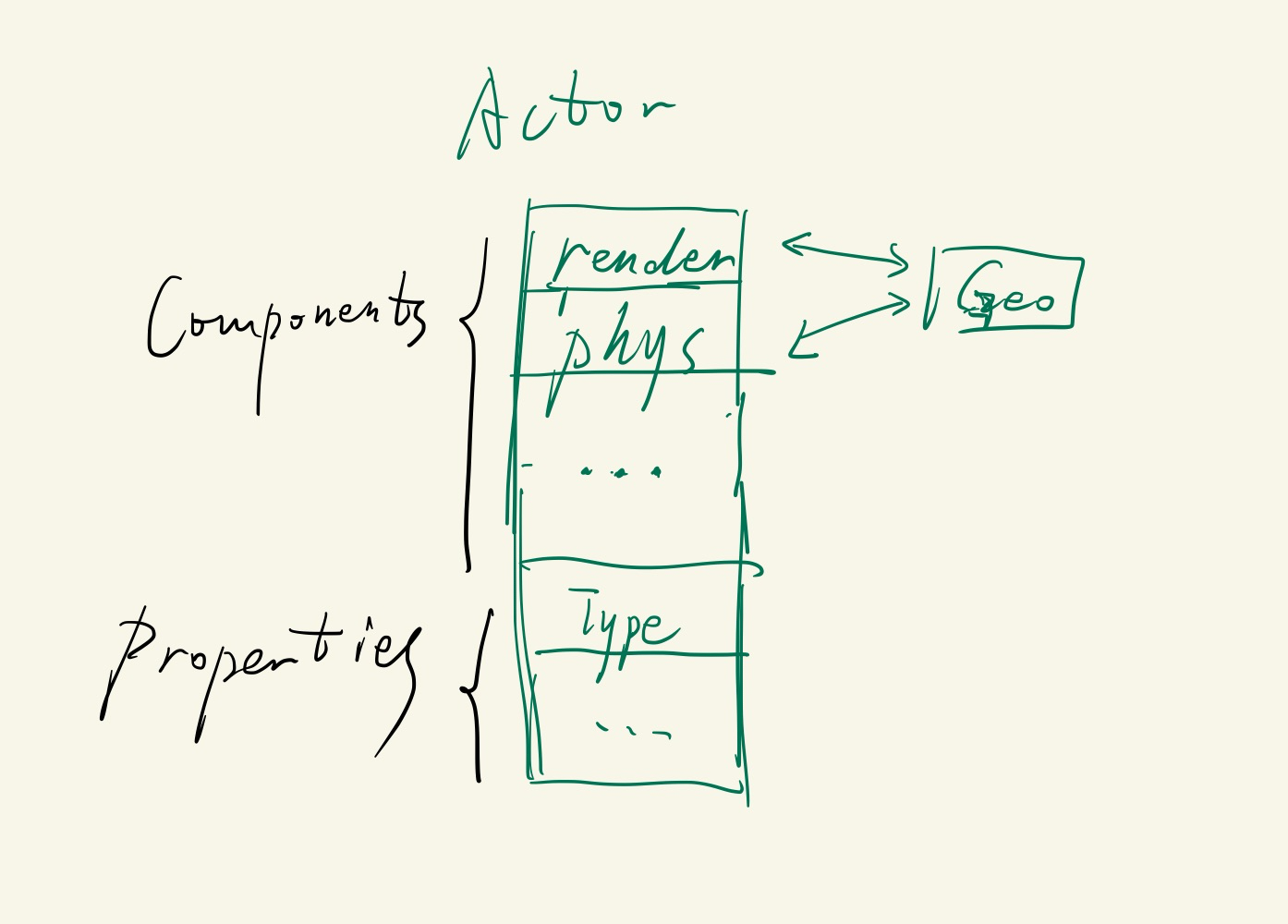
几何模块
BVH
从距离的中点去划分,存在死循环的问题,当一个节点的兄弟节点为空时,就需要递归返回了,否则一个AABB中有n个三角形,划分后变为0 + n, 继续还是0 + n
std::pair<BVHNode*, BVHNode*> SplitBVHNode(BVHNode* node){
// x-alias partition
auto bound = node->bound;
std::vector<Triangle*> leftTriangles, rightTriangles;
leftTriangles.reserve(node->triangles.size());
rightTriangles.reserve(node->triangles.size());
for(const auto& tri : node->triangles){
if(GetMax(GetBound(*tri)).x < bound.position.x){
leftTriangles.push_back(tri);
}else{
rightTriangles.push_back(tri);
}
}
auto left = new BVHNode(GetBound(leftTriangles), std::move(leftTriangles));
auto right = new BVHNode(GetBound(rightTriangles), std::move(rightTriangles));
return {left, right};
}
void RecursiveBuildBVH(BVHNode* node, int kThreshold) {
// Boundary Condition
if(node->triangles.size() < kThreshold){
return;
}
// if(BVH_DEPTH > MAX_DEPTH) return;
PHY_DEBUG("Node bound pos: {}, halfSize: {}, triNum:{}", node->bound.position, node->bound.halfSize, node->triangles.size());
// Split
auto [leftNode, rightNode] = SplitBVHNode(node);
if(!leftNode->triangles.empty() || !rightNode->triangles.empty()){
std::vector<Triangle*>().swap(node->triangles);
}
bool shouldReturn = false;
if(!leftNode->triangles.empty()){
node->left = leftNode;
}else{
shouldReturn = true;
}
if(!rightNode->triangles.empty()){
node->right = rightNode;
}else{
shouldReturn = true;
}
if(shouldReturn) return;
// Recursive
BVH_DEPTH++;
RecursiveBuildBVH(node->left, kThreshold);
BVH_DEPTH--;
BVH_DEPTH++;
RecursiveBuildBVH(node->right, kThreshold);
BVH_DEPTH--;
}
只从x方向取中点去划分也会导致AABB越来越细长

渲染模块
CMakeLists.txt
if(APPLE)
# OPENGL
find_package(OpenGL REQUIRED)
# GLFW
find_package(glfw3 REQUIRED)
target_link_libraries(Renderer PUBLIC OpenGL::GL glfw)
这样就可以了,因为CMake会尝试查找名为FindOpenGL.cmake的模块文件。在本地mac中路径为
~/brew-2.2.2/Cellar/cmake/3.23.2/share/cmake/Modules
里面会设定一些库的名称,比如OpenGL::GL可以直接链接
31 ``OpenGL::GL``
32 Defined to the platform-specific OpenGL libraries if the system has OpenGL .
33 ``OpenGL::GLU``
34 Defined if the system has OpenGL Utility Library (GLU).
35
36 .. versionadded:: 3.10
37 Additionally, the following GLVND-specific library targets are defined:
38
39 ``OpenGL::OpenGL``
40 Defined to libOpenGL if the system is GLVND-based.
41 ``OpenGL::GLX``
42 Defined if the system has OpenGL Extension to the X Window System (GLX).
43 ``OpenGL::EGL``
44 Defined if the system has EGL.
VAO VBO EBO
思路
1 VAO <==> 1 VBO, 1 VEO 用一个GLVertexArray类
将一个GLVertexArray对象绑定一个物体,场景中可以加入多个物体,每个物体负责自己的GLVertexArray的GenBuffer、BufferData、Bind、UnBind
渲染的一个流程大概是:
- 设置渲染参数(比如深度测试、混合测试等)
- 设置MVP矩阵
- ==设置material(包括各种texture)【可以通过工厂模式,读取json】==(SetMaterial)
- 渲染第一帧
- ==mesh ==> [vertices data, indices data]==(GetVerticesBuffer)
- // 以下4个放在一个函数里(SetPipelineData)
- ==生成 VAO, VBO, EBO==
- ==vertices data ==> VBO==
- ==indices data ==> EBO==
- ==设置VAO的vertex attribute pointer, 并enable==
- draw
- RenderLoop
- Update mesh【物理运动】
- 渲染一帧
- ==mesh ==> [vertices data, indices data]==(GetVerticesBuffer)
- ==更新texture, material(可能需要, 只需要更新material,而不用更新shader)==(SetMaterial)
- // 以下4个放在一个函数里(SetPipelineData)
- ==生成 VAO, VBO, EBO==
- ==vertices data ==> VBO==
- ==indices data ==> EBO==
- ==设置VAO的vertex attribute pointer, 并enable==
- draw
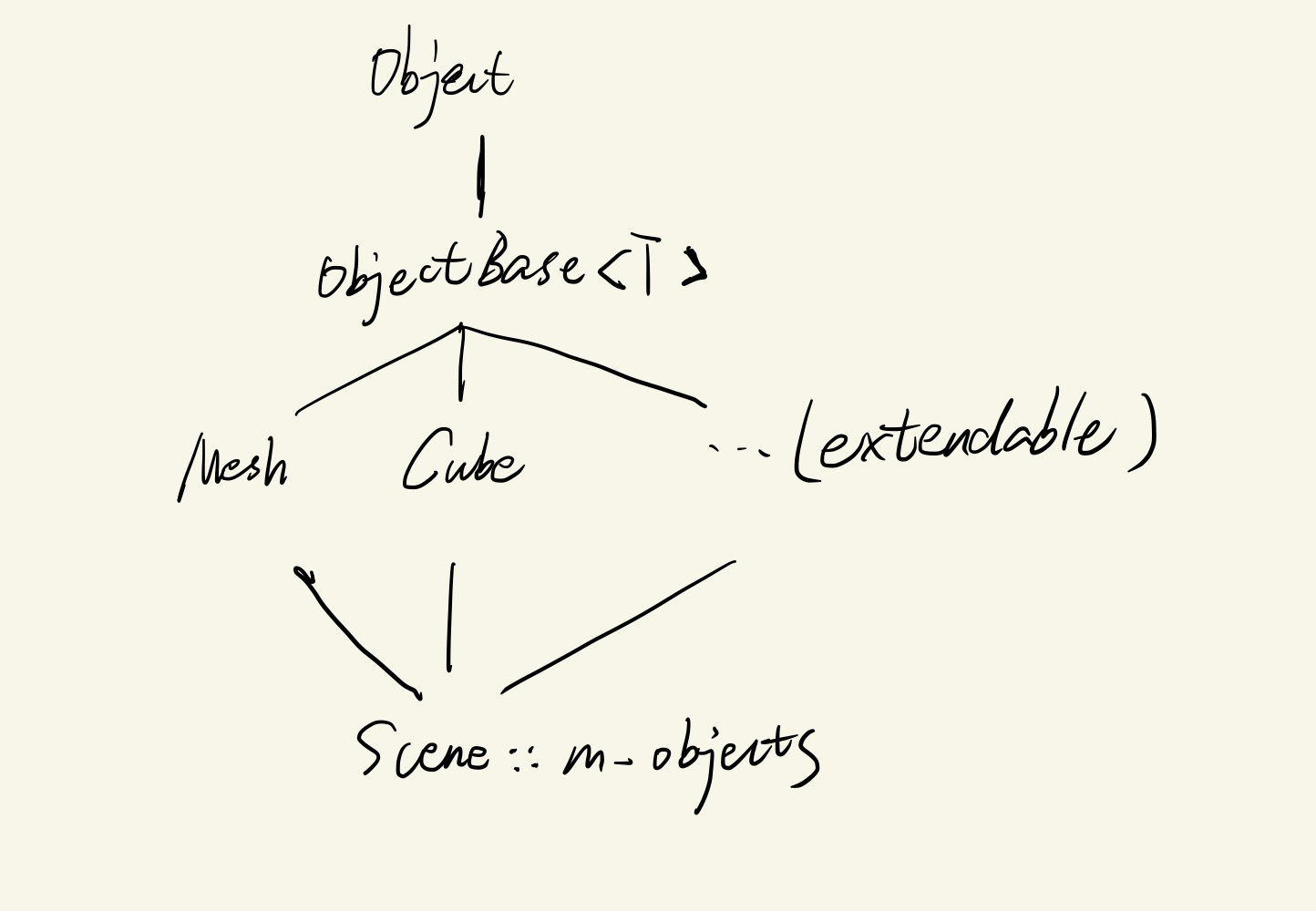
黄色部分写在ObjectBase里, ObjectBase被各种物体继承,比如Mesh, Cube等。
额外套一层Object是为了Scene里可以用std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Object>> m_objects 来实现多态
class Object{
public:
virtual ~Object() = default;
virtual void SetPipelineData() = 0;
virtual void GetVerticesBuffer() = 0;
virtual void SetMaterial() = 0;
};
template<typename VertexType>
class ObjectBase : public Object {
public:
virtual void SetPipelineData() = 0; // Setup VAO, VBO, VEO
virtual void GetVerticesBuffer() = 0; // Get vertices and indices
virtual void SetMaterial() = 0; // Set shader/material parameter/texture
public:
std::vector<VertexType> m_vertices;
std::vector<unsigned int> m_indices;
Shader *m_shader;
GLVertexArray m_VAO{};
};
VertexType用来制定某个物体在渲染管线上,一个节点的格式,在ObjectBase的继承类中设置,方便拓展,比如
struct MeshVertex{
vec3 position;
vec3 normal;
vec2 coord;
};
class Mesh : public ObjectBase<MeshVertex>{
public:
~Mesh() override;
void SetPipelineData() override;
void GetVerticesBuffer() override;
void SetMaterial() override;
private:
std::shared_ptr<geo::Mesh> GeoMesh;
};
虽然我们知道,一个模型,比如*.obj可能由很多个mesh组成,但我们将这种模型抽象为geo::mesh,在geometry中处理变换、缩放等操作,传输给renderer::mesh送上渲染管线。
Physic模块
cloth
implicit solver
注意 下图中的x[0] , v[0]表示第0时刻, x(0)表示newton的初始值
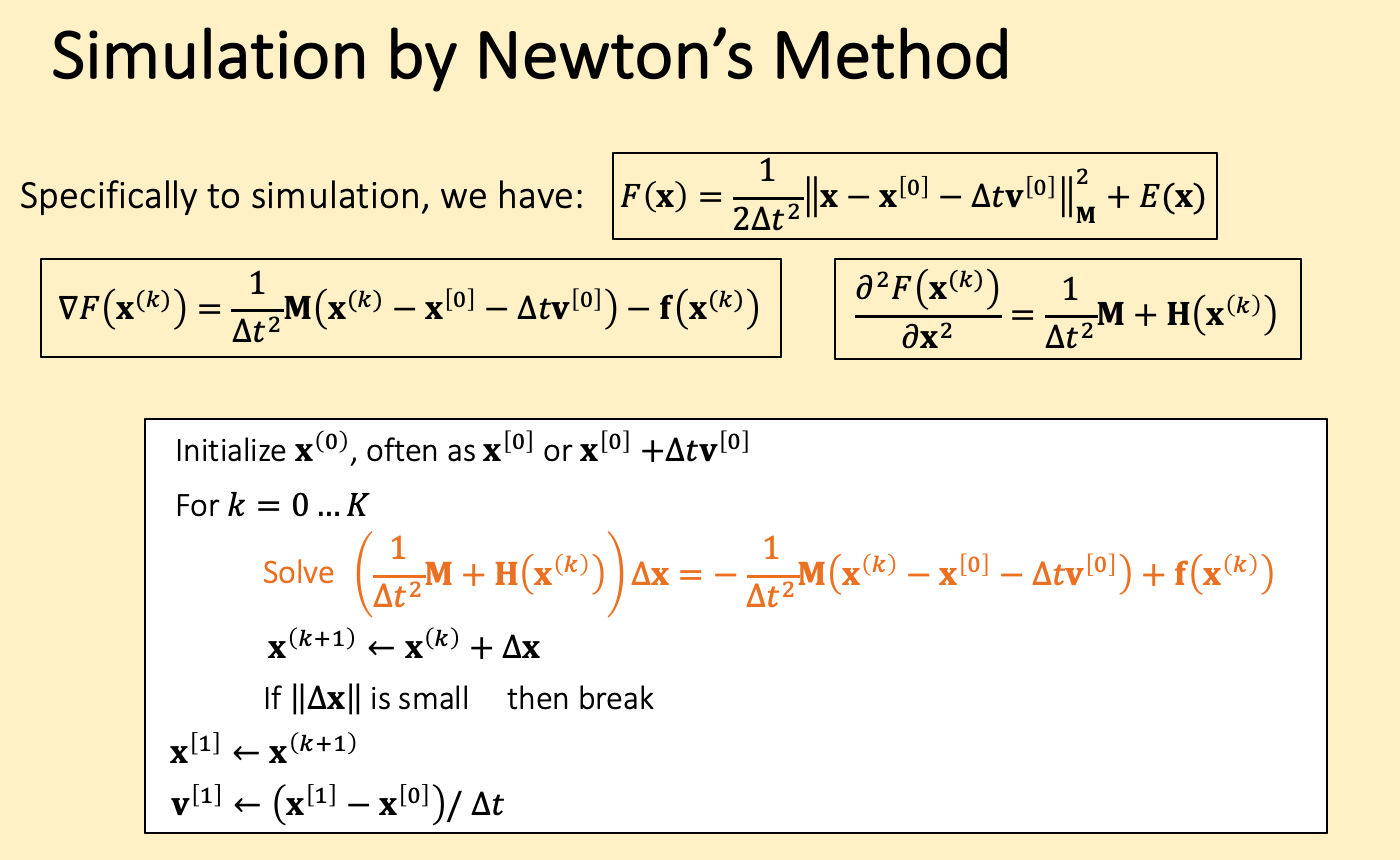
准确的Solve dx应该采用线性系统的解算器,比如jacobi、pcg等,这里用近似, g是一介导, hessian近似位一个对角阵,k是弹簧的K
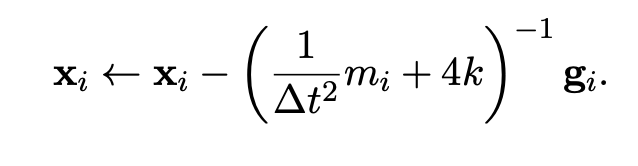
两种初始化区别不大,在设定最大迭代次数位32时,前者为40ms/substep,后者为50ms/substep
优化过程
- 最开始40ms
C++
std::string_view
c++17
std::string s = "123456"; // 会把 c string 常量深拷贝给s
std::string_view s = "123456"; //只包括首位两个指针, 不会拷贝,但read-only
坑
关于Model
以.obj为例,正常的obj file中,vertex是不会重复的,所以vertices.size() < indices.size()
但在load之后,主流的loader(比如assimp的默认参数和tinyobjloader)会把vertex重复来实现两个面的公共顶点具有不同的normal,所以vertices.size() == indices.size()
而我在渲染模块中采取了重复定点的方案,在物理模块使用了不重复的方案(后续优化),所以写了相互转化的函数。
- 不重复 ==> 重复, 这里转成 vector<Triangle*>
auto& triVec = m_model->m_meshes[0].triangles;
triVec.clear();
triVec.reserve(m_indices.size() / 3);
for(int i = 0; i < m_indices.size(); i += 3){
auto tri = new geo::Triangle(
m_vertices[m_indices[i]],
m_vertices[m_indices[i + 1]],
m_vertices[m_indices[i + 2]]
);
triVec.push_back(tri);
- 重复 ==> 不重复
struct Vec3Hash {
size_t operator()(const vec3& v) const {
size_t seed = 0;
std::hash<float> hasher;
seed ^= hasher(v.x) + 0x9e3779b9 + (seed << 6) + (seed >> 2);
seed ^= hasher(v.y) + 0x9e3779b9 + (seed << 6) + (seed >> 2);
seed ^= hasher(v.z) + 0x9e3779b9 + (seed << 6) + (seed >> 2);
return seed;
}
};
std::unordered_map<vec3, int, Vec3Hash> vertexMap;
std::vector<vec3> uniqueVertices;
uniqueVertices.reserve(m_vertices.size());
// 注意要遍历face
for (int i = 0; i < m_indices.size(); i++) {
auto vertIdx = m_indices[i];
auto it = vertexMap.find(m_vertices[vertIdx]);
if (it == vertexMap.end()) {
int newIndex = static_cast<int>(uniqueVertices.size());
vertexMap[m_vertices[vertIdx]] = newIndex;
uniqueVertices.push_back(m_vertices[vertIdx]);
m_indices[i] = newIndex;
} else {
m_indices[i] = vertexMap[m_vertices[vertIdx]];
}
}
uniqueVertices.shrink_to_fit();
m_vertices = std::move(uniqueVertices);
PHY_INFO("after deduplicate: {} vertices, {} indices",
m_vertices.size(), m_indices.size());
拼接mesh
for (const auto &mesh: m_model->m_meshes) {
m_indices.reserve(m_indices.size() + mesh.indices.size());
auto tempSize = m_vertices.size(); // 易错
for(int i = 0; i < mesh.indices.size(); i++){
m_indices.push_back(mesh.indices[i] + tempSize);
}
m_vertices.reserve(m_vertices.size() + mesh.vertices.size());
m_vertices.insert(m_vertices.end(), mesh.vertices.begin(), mesh.vertices.end());
}
switch case
原理是跳转到相应的case往下执行,所以必须加break
switch(x):
case a:
break;
case b:
break;
IMGUI 与 renderer层级
IMGUI面板在顶层,所以放在后面
///////////// physics
m_physics->Update(dt);
///////////// renderer
m_camera.Update(dt);
m_renderer.Update(m_camera);
auto renderList = m_scene->GetObjects();
m_renderer.Render(m_camera, renderList.cbegin(), renderList.cend());
//////////// Gui
m_gui->Draw(m_window.m_window);
鼠标在IMGUI面板上时禁用摄像头转动
在gui类里include Input.h, Input类中声明bool m_mouseClickEnabled, 同时监听鼠标与面板的关系,对m_mouseClickEnabled进行修改,MouseClicked监听事件加入判断
std::function<void(int, int, int)> mouseClicked = [&](auto button, auto action, auto mode){
if(m_mouseClickEnabled && button >= 0 && button < 128){
switch (action){
case GLFW_PRESS:
// PHY_INFO("press");
m_buttons[button] = true;
break;
case GLFW_RELEASE:
m_buttons[button] = false;
// PHY_INFO("release");
break;
}
}
};
gui类内
if (ImGui::IsWindowHovered())
{
// Disable mouse actions by capturing mouse input events
// ImGui::CaptureMouseFromApp(true);
Input::GetInstance().disableMouse();
// Optionally, you can also disable keyboard input events
// ImGui::CaptureKeyboardFromApp(true);
}else{
// Release mouse input events when the mouse is not hovering
// ImGui::CaptureMouseFromApp(false);
Input::GetInstance().enableMouse();
// Optionally, release keyboard input events
// ImGui::CaptureKeyboardFromApp(false);
}
全局变量 static / extern
编译单元就是一个cpp,并且展开里面所有的#include
static 定义本编译单元的全局变量
// Base.h
static int x;
// A.cpp (A 编译单元)
#include <Base.h>
x = 1; // A_x
// B.cpp (B编译单元)
#include <Base.h>
x = 2; // B_x
// A_x和B_x存在两个不同的地址 是不一样的
extern 声明本编译单元或其他编译单元的全局变量
首先是定义和声明的区别
int x; // 定义 未初始化
int y = 1; // 定义 并初始化
extern int x; // 声明
extern int x = 0; // 定义,能编译但一般不这么用
这里的全局,只能用于相互链接的某一个或几个库(STATIC, SHARED都可以)、或executable
相互链接是通过target_link_libraries(lib_a PUBLIC lib_b)
在打包某一个库时,必须保证他用到的全局变量在[这个库或他链接的库内部]定义
add_library(render A.cpp B.cpp C.cpp)
add_library(physic D.cpp)
target_link_libraries(physic render)
// physics只能用render,physics里定义的全局变量
// 而render并不能用physics里定义的全局变量
add_executable(main main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(main render physic)
// main只能用render,physics里定义的全局变量
// 而render,physics并不能用main里定义的全局变量
// case 0
add_executable(main A.cpp B.cpp C.cpp)
// case 1
// D.cpp查找不到A.cpp中定义的全局变量
// Undefined symbols
// 因为physic和render是两个独立的库,所以互相查不到 可以通过target_link_libraries(physic render)解决
add_library(render A.cpp B.cpp C.cpp)
add_library(physic D.cpp)
add_executable(main main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(main render physic)
// case 2
// 可以的 因为main链接了render库
add_library(render A.cpp B.cpp C.cpp)
add_executable(main main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(main render)
在某一个模块里定义一个全局变量,在本模块或其他模块使用这个全局变量需要声明
- 必须在cpp中定义全局变量,否则可能会redefinition error
// A.cpp
int x; // 注意这是定义,只是没有初始化
void f(){
x = 5;
}
// B.cpp
extern int x; // 加了extern表示声明
x = 6;
// C.cpp
extern int x; // 加了extern表示声明
std::cout << x;
- 在header中声明,用于简化
// A.cpp
int x; // 注意这是定义,只是没有初始化
void f(){
x = 5;
}
// Base.h
extern int x;// 加了extern表示声明
// B.cpp
#include <Base.h>
x = 6;
// C.cpp
#include <Base.h>
std::cout << x;
- 在header中定义的话
////// 正确
// A.h
extern int x; // 声明 在本模块或其他模块存在x的定义
// A.cpp
#include "A.h"
int x = 5;
int main(){
std::cout << x;
}
////// 错误 redifinition
// A.h
extern int x = 0; // 这是定义
// A.cpp
int x = 5;
int main(){
std::cout << x;
}
实践
在demo里定义全局变量,控制imgui事件对渲染、仿真结果做出改变
// demo.cpp
// 定义只在demo.cpp会用到的变量
namespace control{
static geo::BVHNode* currNode;
static vec3 ground_color = {0.2, 0.4, 0.6};
static vec3 ground_pos = vec3(0, -1.2, 0);
static vec3 ground_halfSize = vec3(100, 1.2, 100);
static int show_level = 10;
}
// 声明需要去外部找的变量
namespace control{
extern vec4 clear_color;
extern geo::BVHSplitStrategy bvh_strategy;
}
void f(){control::clear_color ....}
// RenderSystem.cpp
// 声明需要去外部找的变量
namespace control{
extern vec4 clear_color;
}
void f(){control::clear_color ....}
// GuiSystem.cpp
// 定义全局变量
namespace control{
vec4 clear_color = vec4(0.45f, 0.55f, 0.60f, 1.00f);
}
// 包含关系
add_library(Gui GuiSystem.cpp)
add_library(RenderSystem RenderSystem.cpp)
target_link_libraries(RenderSystem Gui)
add_executable(demo demo.cpp)
target_link_libraries(demo RenderSystem Gui)
虚函数
Derived类的第一个虚函数必须定义,只声明不定义会报错
Undefined symbols for architecture x86_64:
"vtable for Cloth", referenced from:
ActorBase<geo::Model>::InitPhysicsObject() in BVHTest.cpp.o
NOTE: a missing vtable usually means the first non-inline virtual member function has no definition.
虚函数的默认参数不会被继承,通过什么类型的指针调用,就会用对应的默认参数
opengl
glDrawElement 如果画的是三角形primitive,并且ebo出现 (1,1,0)这样重复的顶点会报错
Texture uv坐标
stb_image读取的图片和opengl渲染管线读入的 y坐标要返转一下
m_coord[i] = vec2(vertices[i].TextureCoordinate.X,
1- vertices[i].TextureCoordinate.Y);